At this point, we know how to install Cilium and create a BGP peering with our routers. Now we need to let the outside world reach our Kubernetes apps.
If you don’t have the KinD cluster with Cilium go to https://arielantigua.com/weblog/2024/07/cilium-bgp-lab-locally/
When using Cilium you can reach an application using the Pod IP address or using a LoadBalance IP assigned to a Service. In the previous article we only advertised the Pod Address to our BGP neighbors, lets add more stuff so we can be close to a real deployment.
If you already have cloned the repo, go and do a pull so you can get the new config files and other stuff in the Makefile, or better yet, go and do a new clone of the repo and start from scratch, that’s the idea of the repo!
New stuff in this LAB.
-
-
- serviceSubnet in cluster.yaml (10.2.0.0/16)
- serviceSelector in the CiliumBGPPeeringPolicy (service = public), this useful to identify what LoadBalancer will be announced by this peering policy.
- public-pool.yaml with the configuration for the LoadBalancer IP Pool.
- If you look at the topo.yaml file, will find a new Linux node (client0) for testing, this is based on alpine:latest, will test reachability to our LoadBalancer IP from this container that is connected to tor1 with IP address 10.0.100.2/24
- Bookinfo application so we can have something to reach from client0.
-
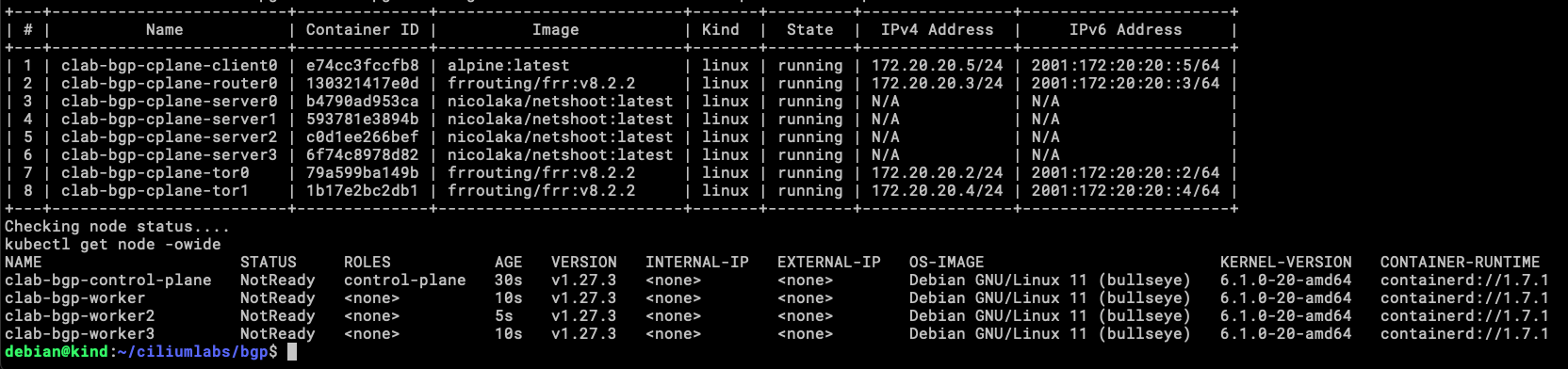
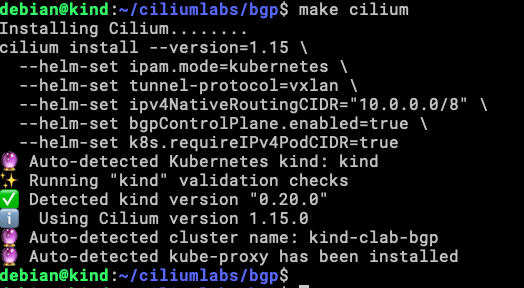
Now let’s build the environment, just like before, running make will create a KinD cluster with 4 nodes (1 control-plane and 3 workers), a containerlab topology with 3 routers (FRR), and 1 client (Alpine). decide to let alone the Cilium install manually or with make cilium, in case there is a need to do something different with the same KinD cluster or add another option to Cilium at install time.
This is the result of running make, as you can see in the image, now you can go and install Cilium in whatever way you like the most, in this case, I will use these options:
cilium install --version=1.15 \ --helm-set ipam.mode=kubernetes \ --helm-set tunnel-protocol=vxlan \ --helm-set ipv4NativeRoutingCIDR="10.0.0.0/8" \ --helm-set bgpControlPlane.enabled=true \ --helm-set k8s.requireIPv4PodCIDR=true
The fastest way is to do this: make cilium
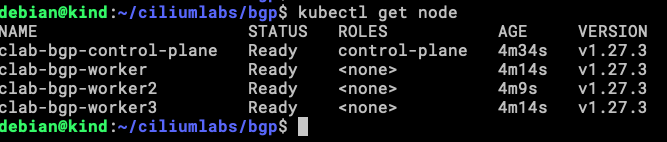
The nodes are ready for workloads.
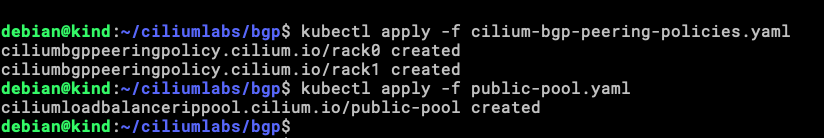
Now is the time to apply both, the CiliumBGPPeeringPolicy and the CiliumLoadBalancerIPPool.
You can do it with make or the official way with kubectl.
kubectl apply -f cilium-bgp-peering-policies.yaml kubectl apply -f public-pool.yaml
You can validate the configurations with the following commands.
kubectl get -f cilium-bgp-peering-policies.yaml -oyaml kubectl get -f public-pool.yaml -oyaml
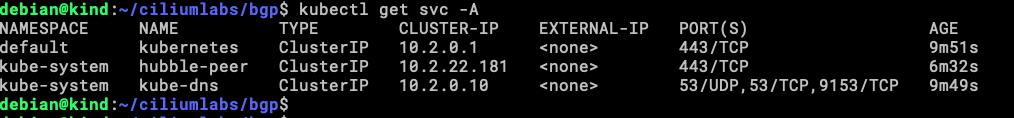
Our lab environment is ready to assign IP to LoadBalancer services, lest check the existing ones first.
Is time to deploy our test application.
Now there is an app in the repo, you can deploy the bookinfo application, which is used by Istio to do some demos, I just cloned it and added a Service to pick up an Address from our IP Pool and advertised it to the Tor(0,1) routers.
https://github.com/aredan/ciliumlabs/tree/main/bookinfo/kustomize
kubectl apply -k kustomize
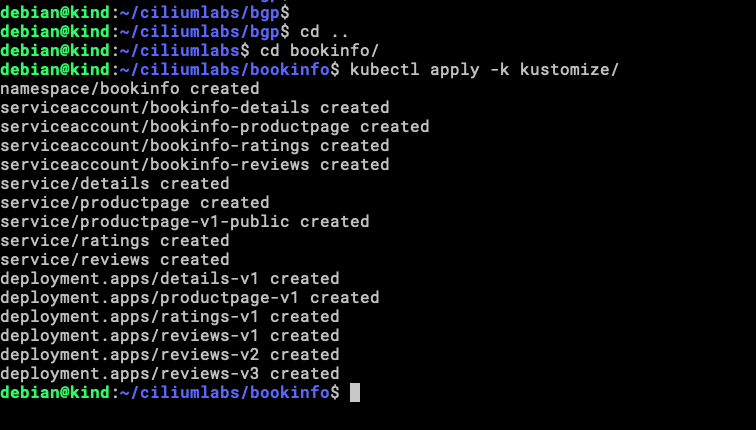
Let’s check the Services that we have now.
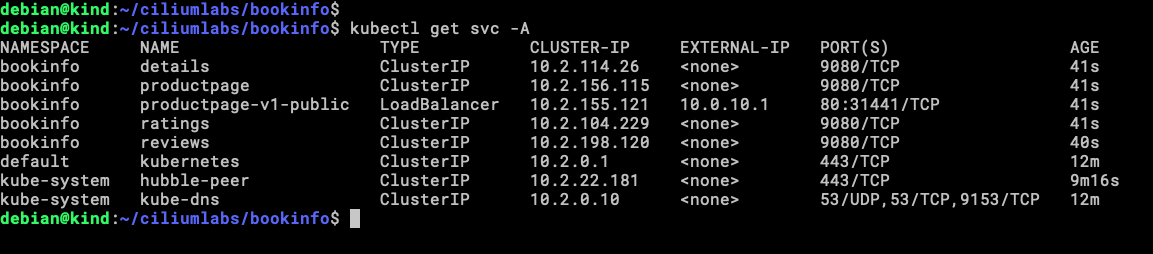
There is our LoadBalancer IP address (10.0.10.1) and others ClusterIP, the LoadBalancer is the one that we will be testing from client0.
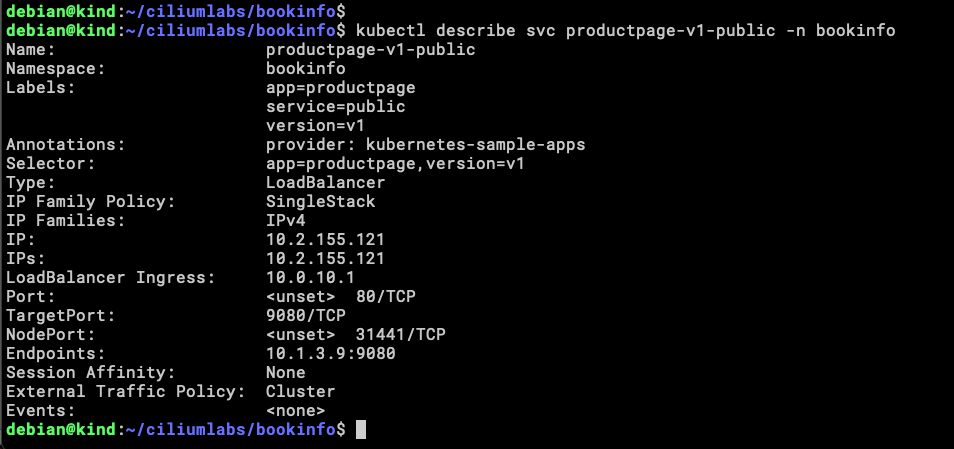
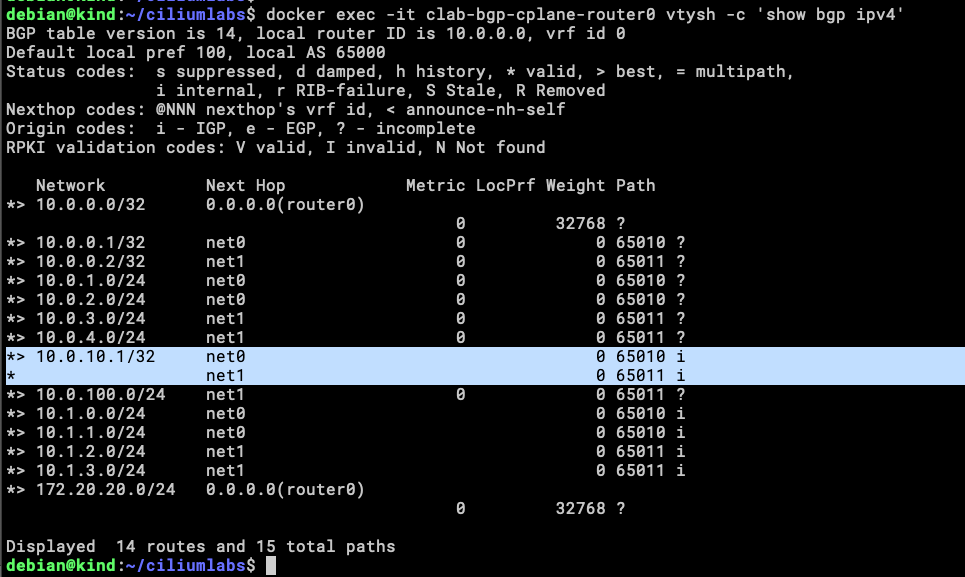
We can see there is an IP assigned to the Service, but is better if we can validate that this address is being announced to the Tor routers.
docker exec -it clab-bgp-cplane-router0 vtysh -c 'show bgp ipv4'
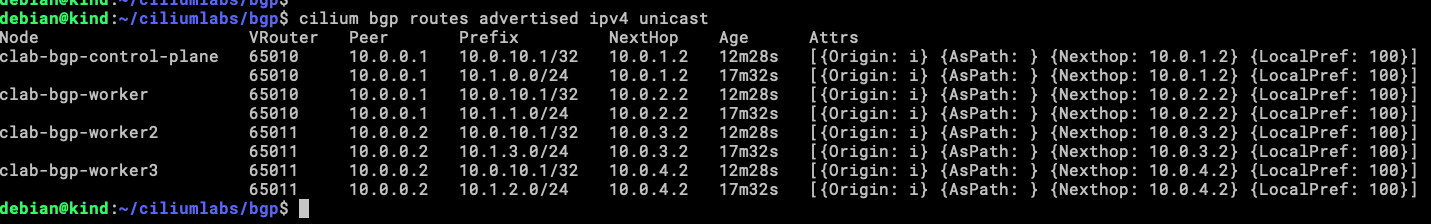
Also, from Cilium itself we can validate that his address is being announced from the virtualRouters.
Within the Cilium CLI exists a subcommand called bgp (hard to pass!!) and with this, we can validate a few things.
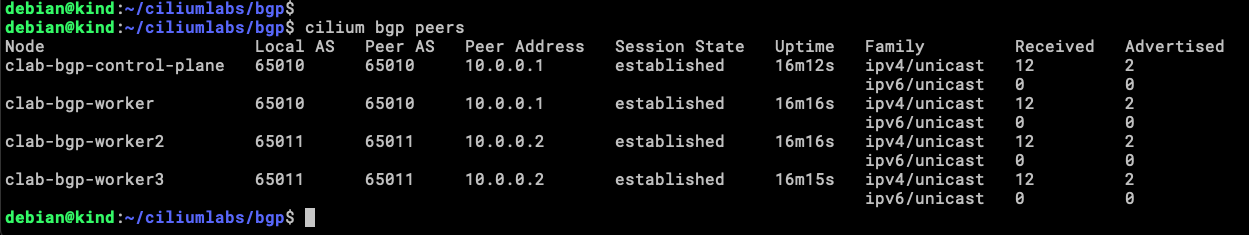
cilium bgp routes advertised ipv4 unicast
Our four nodes are announcing the same address to upstream routers, this is because of the trafficPolicy assigned to the service.
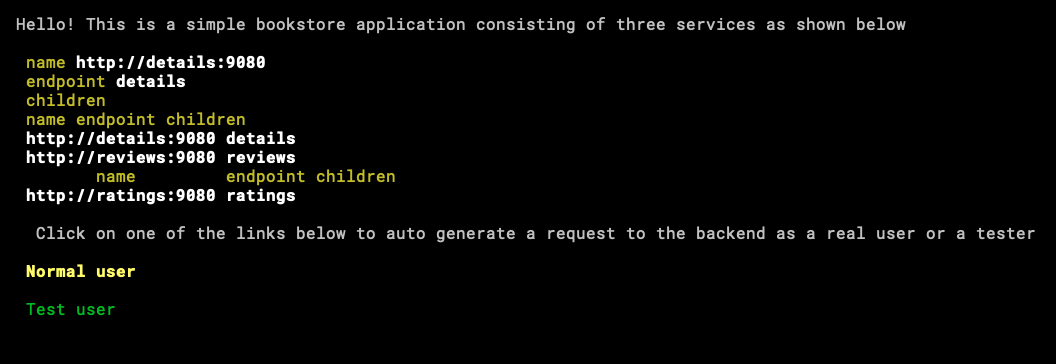
Is time to reach our App.
We need to get into client0 container, this is an alpine container so ash is the shell.
Installing curl and Lynx. In case you don’t know what Lynx is, is a console browser, this feels like traveling to the past when the one that stayed more in the console was the strongest.
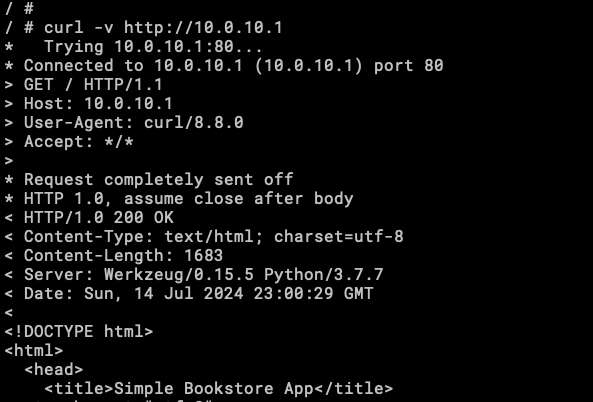
We can see that curl is reaching the app, this way is hard to interact we the application, now with Lynx!
lynx http://10.0.10.1
Isovalent (Cilium creators) announced new support for ClusterIP in BGP !!